目标检测
基础概念
Anchor Box
提出的动机:想让一个grid cell检测出多个物体(针对有重叠的物体)
怎么实现的?
预先定义两个不同形状的Box,然后把预测结果和这两个box联系起来,在预测结果向量中一通输出
Each object in traing image is assigned to grid cell thant contains that object’s midpoint and anchor box for the grid cell with highest IoU
(grid cell, anchor box )
R-CNN系列
Fast R-CNN
https://blog.csdn.net/lanran2/article/details/60143861
Faster R-CNN
RPN
RPN是什么?
An RPN is a fully-convolutional network that simultaneously predicts object bounds and objectness scores at each position.
RPN share convolutional layers with state-of-the-art object detection networks. By sharing convolutions at test-time, the marginal cost for computing proposals is small.
Feature Pyramid Networks
FPN is not an object detector by itself. It is a feature detector that works with object detectors.
ConvNet为什么比传统的视觉方法好?
ConvNets being capable of representing higher-level semantics, robust to variance in scale.
in-network feature hierarchy为什么有问题
This in-network feature hierarchy produces feature maps of different spatial resolutions, but introduces large semantic gaps caused by different depths. The high-resolution maps have low-level features that harm their representational capacity for object recognition.
一句话描述FPN在做什么?
In other words, we show how to create in-network feature pyramids that can be used to replace featurized image pyramids without sacrificing representational power, speed, or memory.
FPN leverage了什么?
On the contrary, our method leverages the architecture as a feature pyramid where predictions (e.g., object detections) are independently made on each level.
Our goal is to leverage a ConvNet’s pyramidal feature hierarchy, which has semantics from low to high levels, and build a feature pyramid with high-level semantics throughout.
网络构造方式
The construction of our pyramid involves a bottom-up pathway, a top-down pathway, and lateral connections.
Bottom-up pathway
Bottom指图片
术语: stage
There are often many layers producing output maps of the same size and we say these layers are in the same network stage.
术语: pyramid level
For our feature pyramid, we define one pyramid level for each stage.
为什么选每个stage中的最后一层作为feature maps set的reference ?
We choose the output of the last layer of each stage as our reference set of feature maps, which we will enrich to create our pyramid. This choice is natural since the deepest layer of each stage should have the strongest features.
Top-down pathway & lateral connections
The topdown pathway hallucinates higher resolution features by upsampling spatially coarser, but semantically stronger, feature maps from higher pyramid levels.
lateral connections的作用?
These features( spatially coarser, but semantically stronger, feature map ) are then enhanced with features from the bottom-up pathway via lateral connections.
Each lateral connection merges feature maps of the same spatial size from the bottom-up pathway and the top-down pathway.
bottom-up feature map的特点
The bottom-up feature map is of lower-level semantics, but its activations are more accurately localized as it was subsampled fewer times.
top-down feature maps是怎么构建的?
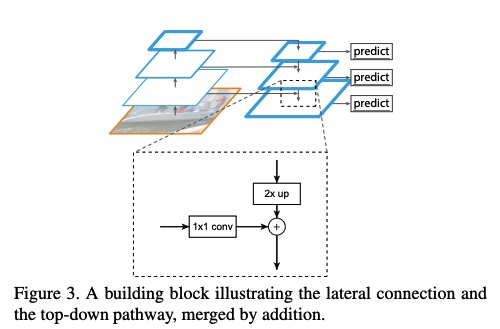
With a coarser-resolution feature map, we upsample the spatial resolution by a factor of 2 (using nearest neighbor upsampling for simplicity). The upsampled map is then merged with the corresponding bottom-up map (which undergoes a 1×1 convolutional layer to reduce channel dimensions) by element-wise addition.
Finally, we append a 3×3 convolution on each merged map to generate the final feature map, which is to reduce the aliasing effect of upsampling.

应用
for RPN(Faster R-CNN)
We adapt RPN by replacing the single-scale feature map with our FPN.
anchors 是什么意思?
一些不同形状的框
we extract multiple feature map layers with FPN and feed them into an RPN (an object detector using convolutions and anchors) in detecting objects. RPN applies 3 × 3 convolutions over the feature maps followed by separate 1 × 1 convolution for class predictions and boundary box regression. These 3 × 3 and 1 × 1 convolutional layers are called the RPN head. The same head is applied to all feature maps.

for Fast-RCNN
To use it with our FPN, we need to assign RoIs of different scales to the pyramid levels.
Fast R-CNN and Faster R-CNN data flow
It works with one feature map layer to create ROIs. We use the ROIs and the feature map layer to create feature patches to be fed into the ROI pooling.

In FPN, we generate a pyramid of feature maps. We apply the RPN (described in the previous section) to generate ROIs. Based on the size of the ROI, we select the feature map layer in the most proper scale to extract the feature patches.

The formula to pick the feature maps is based on the width w and height h of the ROI.


So if k = 3, we select P3 as our feature maps. We apply the ROI pooling and feed the result to the Fast R-CNN head (Fast R-CNN and Faster R-CNN have the same head) to finish the prediction.
框架设计中元素的作用
top-down enrichment发挥了什么作用?
We conjecture that this is because there are large semantic gaps between different levels on the bottom-up pyramid .
The top-down pyramid has strong semantic features and fine resolutions.
lateral connections发挥了什么作用?
This top-down pyramid has strong semantic features and fine resolutions. But we argue that the locations of these features are not precise, because these maps have been downsampled and upsampled several times. More precise locations of features can be directly passed from the finer levels of the bottom-up maps via the lateral connections to the top-down maps.
金字塔的表现方式有多重要?
pyramid levels can increase its robustness to scale variance.
其他人的解读
Mask R-CNN
- ROI Align
https://www.quora.com/How-does-ROTAlign-work-in-Mask-RCNN
Focal Loss
https://towardsdatascience.com/retinanet-how-focal-loss-fixes-single-shot-detection-cb320e3bb0de
https://github.com/fastai/fastai/blob/master/courses/dl2/pascal-multi.ipynb